Introduction
It often begins subtly—a flicker of strange colors where there should be none, a ghostly polygon in a rendering, or a momentary screen tear during a critical computation. For anyone relying on GPU power, that first sign of a problem triggers a wave of anxiety. But for an AI enterprise in the middle of training a large language model that has already consumed weeks of work and thousands of dollars in compute time, this isn’t just an annoyance; it’s a potential catastrophe. These visual glitches, known as GPU artifacting, are the visible symptoms of a deeper, more serious hardware issue.
In the high-stakes world of artificial intelligence, where model training runs can last for weeks and inference services must be always-on, hardware stability isn’t a nice-to-have—it’s non-negotiable. A single faulty GPU can corrupt a dataset, crash a training job, or bring a production AI service to its knees, resulting in massive financial loss and project delays. This is why understanding GPU artifacting is crucial, and more importantly, why building your AI infrastructure on a stable, reliable foundation is paramount. This is the very problem platforms like WhaleFlux are built to solve, providing AI enterprises with access to rigorously tested, high-performance GPU power that they can count on, day in and day out.
Section 1: What is GPU Artifacting? Recognizing the Signs
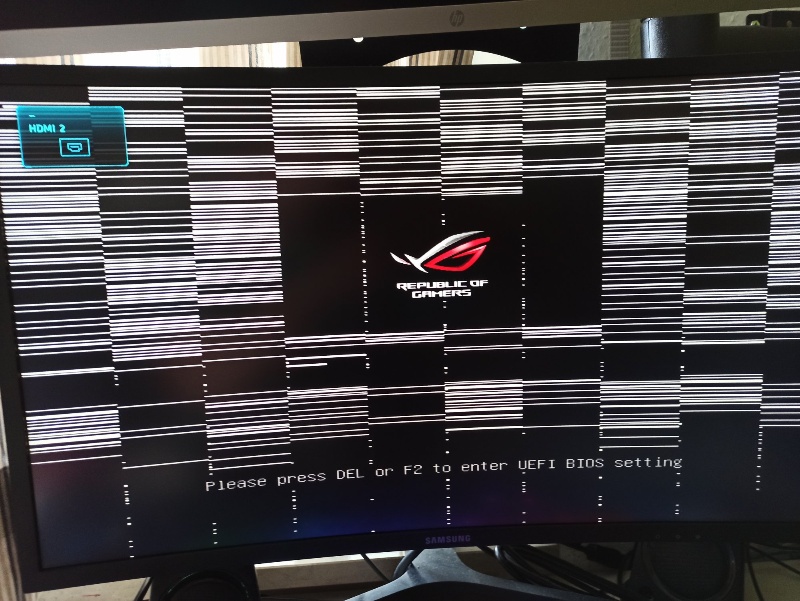
In simple terms, GPU artifacting refers to any kind of visual distortion or on-screen abnormality that occurs when the graphics processing unit fails to correctly process or render data. Think of the GPU as a meticulous artist. When it’s healthy, it paints a perfect, precise digital picture. When it’s struggling, it starts making mistakes—dropping colors, drawing lines in the wrong places, or leaving parts of the canvas blank. These mistakes are “artifacts.”
Common GPU artifacting examples include:
- Strange Colors and Ghosting: Unexpected color shifts, bright flashing pixels, or faint “ghost” images trailing behind objects.
- Screen Tearing and Glitches: Horizontal lines splitting the screen or random pixels “sparkling” like static.
- Random Polygons and Texture Corruption: Large, geometric shapes appearing out of nowhere, or surfaces displaying distorted, mismatched textures.
While these symptoms are often discussed by gamers, their implications in a deep learning context are far more severe. During AI workloads, the GPU isn’t just rendering a frame for a game; it’s performing billions of calculations to adjust the parameters of a neural network. GPU artifacting during this process is a critical red flag. It indicates that the GPU is potentially corrupting the very calculations your model’s life depends on, leading to failed training jobs, inaccurate results, and a tremendous waste of time and resources.
Section 2: Common Causes of GPU Artifacting in Compute Environments
To prevent GPU artifacting, you must first understand what causes it. In the demanding environment of an AI data center, the primary culprits are:
Overheating:
This is the most common cause. AI workloads push GPUs to 100% utilization for days or weeks at a time. In a densely packed server rack, inadequate cooling can cause the GPU’s core or, more critically, its VRAM (Video RAM) to overheat. When memory chips get too hot, they cannot hold data reliably, leading to corruption and artifacts.
Overclocking and Instability:
In a bid to squeeze out more performance, some users overclock their GPUs, pushing them beyond the manufacturer’s guaranteed stable limits. While this might offer a short-term speed boost, it dramatically increases the risk of instability and GPU artifacting, as the hardware is operating outside its safe electrical specifications.
Faulty Hardware and VRAM Decay:
Like all electronics, GPUs can have manufacturing defects or simply wear out over time. The constant heating and cooling cycles during intense compute tasks can eventually degrade the solder connections between the GPU chip and the board or cause microscopic failures in the VRAM. This physical decay is a leading cause of persistent artifacting.
Inadequate or Unstable Power Supply:
GPUs like the NVIDIA H100 and A100 are incredibly power-hungry. If the power supply unit (PSU) in a server is insufficient, unstable, or of poor quality, it can deliver “dirty” power with voltage fluctuations. This instability can prevent the GPU from functioning correctly and is a common source of mysterious crashes and artifacts.
Section 3: How to Test for and Diagnose GPU Artifacting
If you suspect a GPU is failing, a systematic GPU artifacting test is essential. For an AI team, this diagnostic process can help isolate a problematic node before it ruins a valuable training run.
Visual Inspection and Monitoring:
The first line of defense is vigilance. Many modern AI and visualization tools will display visual output. Keep an eye out for any of the GPU artifacting examples mentioned earlier during workload execution. Many data center management tools also provide remote console views that can be monitored for glitches.
Stress Testing:
This is the most direct method. Tools like NVIDIA’s own nvidia-smi can be used to monitor basic health stats, while more intensive utilities like FurMark or OCCT are designed to push the GPU to its absolute limits. By applying a maximum computational load, these tools can quickly reveal instability that might not appear under lighter workloads. If a GPU is going to artifact, a stress test will likely trigger it within minutes.
Monitoring Tools:
Proactive monitoring is better than reactive testing. Use hardware monitoring software to keep a constant log of your GPU’s core temperature, memory junction temperature (a critical metric for AI workloads), and power draw. A GPU that is consistently running at its thermal throttle limit (often around 85-95°C for the core and 100-110°C for the memory) is a prime candidate for future failure and artifacting.
It’s worth noting that a rigorous testing and “burn-in” process is a standard part of onboarding any new hardware into a professional environment. On a platform like WhaleFlux, every GPU in our fleet undergoes this kind of intensive stress testing before it is made available to clients, ensuring that the underlying hardware meets our strict stability standards.
Section 4: How to Fix GPU Artifacting and Prevent It in Your AI Fleet
When you encounter GPU artifacting, a tiered approach to how to fix GPU artifacting is the most practical.
Immediate Mitigation Steps:
- Check Cooling: Ensure all fans are working and air filters are clean. Improve case or server rack airflow.
- Reduce Clock Speeds: If the GPU is overclocked, revert it to stock settings. You can even try a slight underclock to enhance stability.
- Update Drivers: While less common for persistent artifacting, ensure you are using the latest, most stable drivers from NVIDIA.
The Ultimate Solution for Businesses:
For an AI company, time is money. The most effective and ultimately cost-saving solution for a GPU that is consistently artifacting is to replace it. Spending dozens of engineer-hours to diagnose and baby a faulty piece of hardware is a terrible return on investment. The downtime and risk of corrupted work far outweigh the cost of a replacement.
This is where the value of a managed service becomes clear. Instead of dealing with the hassle and expense of hardware procurement, testing, and maintenance in-house, a proactive strategy is to leverage a platform that guarantees hardware reliability. WhaleFlux provides a direct path to this peace of mind. We offer access to a verified and maintained fleet of high-end NVIDIA GPUs—including the H100, H200, A100, and RTX 4090. When you use our platform, you are not just renting compute time; you are investing in a infrastructure layer where hardware stability is our responsibility, not your problem.
Section 5: Ensuring Stability with WhaleFlux’s Managed GPU Infrastructure
For an AI enterprise, the goal is to focus on algorithms and models, not on troubleshooting hardware failures. WhaleFlux is designed to be the rock-solid foundation that makes this focus possible, systematically eliminating the risks associated with GPU artifacting.
We ensure stability through several key practices:
Curated and Rigorously Tested Hardware:
Every GPU in the WhaleFlux fleet is put through a stringent vetting process before it enters our inventory. We perform extended stress tests and thermal validation to weed out any units that show the slightest sign of instability. This means the GPUs available for rent or purchase—from the flagship H100 to the versatile A100—arrive pre-certified for reliable performance under sustained AI workloads.
An Optimized Physical Environment:
GPU artifacting often stems from poor cooling or power delivery. WhaleFlux infrastructure is built from the ground up in professional data centers designed for high-density computing. Our servers are equipped with advanced cooling systems and robust, redundant power supplies that provide clean, stable electricity. This optimized environment directly attacks the root causes of overheating and power-related instability.
Focus on AI, Not IT:
The most significant value we provide is freedom from infrastructure headaches. By renting or purchasing reliable GPUs through WhaleFlux, your team of data scientists and ML engineers can dedicate 100% of their energy to building and deploying models. We handle the hardware, the drivers, and the cluster management, offering a streamlined platform that accelerates the deployment of large language models with enhanced stability. Our rental model, with a minimum commitment of one month, is specifically designed to foster this kind of stable, long-term development cycle, as opposed to the chaotic, short-term environment of hourly rentals.
Conclusion
GPU artifacting is more than a visual glitch; it is a serious warning siren blaring from a critical piece of your AI infrastructure. It signals instability that can lead to corrupted data, wasted computational resources, and costly project delays. While knowing how to test for and diagnose GPU artifacting is a valuable skill for any tech team, the most strategic approach for a growing AI enterprise is to build upon a foundation that is designed to prevent these issues altogether.
The future of AI will be built by those who can execute reliably at scale. This requires computational resources that are as dependable as the ideas they power. WhaleFlux provides this essential stability. By offering access to a managed fleet of high-performance NVIDIA GPUs that are professionally maintained and monitored, we allow businesses to bypass the risks of hardware failure and focus on what they do best: driving innovation.