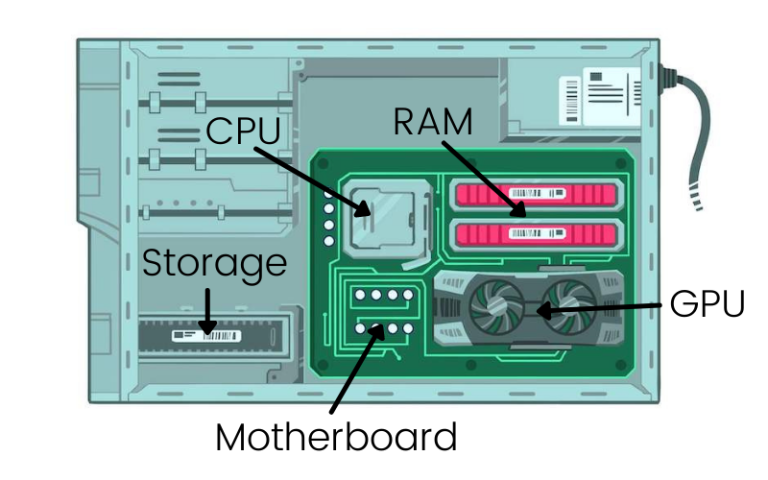
1. The Silent AI Killer: Understanding CPU-GPU Bottlenecks
Imagine your $40,000 NVIDIA H100 GPU running at 30% capacity while its fans sit idle. This isn’t a malfunction – it’s a CPU-GPU bottleneck, where mismatched components throttle performance. Like pairing a sports car with a scooter engine, even elite GPUs (H100/H200/A100/RTX 4090) get strangled by undersized CPUs. For AI enterprises, bottlenecks waste more money than hardware costs. WhaleFlux solves this through holistic optimization that synchronizes every component in your AI infrastructure.
2. Bottleneck Calculators Demystified: Tools & Limitations
What Are They?
Online tools like GPU-CPU Bottleneck Calculator suggest pairings: “Use Ryzen 9 7950X with RTX 4090”. Simple for gaming – useless for AI.
Why They Fail for AI:
- Ignore Data Pipelines: Can’t model CPU-bound preprocessing starving H100s
- Cluster Blindness: No support for multi-node GPU setups
- Memory Oversights: Ignore RAM bandwidth limits
- Real-Time Dynamics: Static advice ≠ fluctuating AI workloads
DIY Diagnosis:
Run nvidia-smi + htop:
- GPU utilization <90% + CPU cores at 100% = Bottleneck Alert!
3. Why AI Workloads Amplify Bottlenecks
AI intensifies bottlenecks in 3 ways:
Data Preprocessing:
- CPU struggles to feed data to 8x H100 cluster → $300k in idle GPUs
Multi-GPU Chaos:
- One weak CPU node cripples distributed training
Consumer-Grade Risks:
- Core i9 CPU bottlenecks even a single A100 by 40%
Cost Impact: 50% performance loss = $24k/month wasted per H100 pod
4. The Cluster Bottleneck Nightmare
Mixed hardware environments (H100 + RTX 4090 + varying CPUs) create perfect storms:
plaintext
[Node 1: 2x H100 + Xeon W-3375] → 95% GPU util
[Node 2: RTX 4090 + Core i7] → 34% GPU util (BOTTLENECK!)
- “Doom the Dark Ages” Effect: Engineers spend weeks manually tuning hardware ratios
- Calculators Collapse: Zero tools model heterogeneous AI clusters
5. WhaleFlux: Your AI Bottleneck Destroyer
WhaleFlux eliminates bottlenecks through intelligent full-stack orchestration:
Bottleneck Solutions:
Dynamic Load Balancing:
- Auto-pairs LLM training jobs with optimal CPU-GPU ratios (e.g., reserves Xeon CPUs for H100 clusters)
Pipeline Optimization:
- Accelerates data prep to keep H100/H200/A100 fed at 10GB/s
Predictive Scaling:
- Flags CPU shortages before GPUs starve: “Node7 CPU at 98% – scale preprocessing”
Unlocked Value:
- 95% GPU Utilization: 40% lower cloud costs for H100/A100 clusters
- 2x Faster Iteration: Eliminate “waiting for data” stalls
- Safe Hybrid Hardware: Use RTX 4090 + consumer CPUs without bottlenecks
6. The WhaleFlux Advantage: Balanced AI Infrastructure
WhaleFlux optimizes any NVIDIA GPU + CPU combo:
| GPU | Common CPU Bottleneck | WhaleFlux Solution |
| H100/H200 | Xeon Scalability limits | Auto-distributes preprocessing |
| A100 | Threadripper contention | Priority-based core allocation |
| RTX 4090 | Core i9 throttling | Limits concurrent tasks |
Acquisition Flexibility:
- Rent Balanced Pods: H100/H200 systems with optimized CPU pairings (1-month min rental)
- Fix Existing Clusters: Squeeze 90% util from mismatched hardware
7. Beyond Calculators: Strategic AI Resource Management
The New Reality:
Optimal AI Performance = Right Hardware + WhaleFlux Orchestration
Final Truth: Unmanaged clusters waste 2x more money than hardware costs.
Ready to destroy bottlenecks?
1️⃣ Audit your cluster for hidden CPU-GPU mismatches
2️⃣ Rent optimized H100/H200/A100 systems via WhaleFlux (1-month min)
Stop throttling your AI potential. Start optimizing.
FAQs
1. What is a CPU-GPU bottleneck in AI workloads, and does it affect WhaleFlux-managed NVIDIA GPU clusters?
A CPU-GPU bottleneck occurs when the CPU (data processing/scheduling) and NVIDIA GPU (parallel computing for AI tasks) operate at mismatched speeds, causing one component to idle while waiting for the other. Common scenarios include: the CPU struggling to feed data fast enough to a high-performance GPU (e.g., H200/A100), or the GPU being underutilized because the CPU can’t preprocess data (e.g., for LLMs) efficiently.
Yes, it affects WhaleFlux-managed NVIDIA GPU clusters – bottlenecks stem from hardware mismatches or unoptimized workflows, not WhaleFlux itself. The tool is designed to detect and resolve these gaps, ensuring NVIDIA GPUs (from RTX 4090 to H200) operate in sync with CPUs for maximum AI efficiency.
2. What are the core causes of CPU-GPU bottlenecks in NVIDIA GPU-based AI deployments?
Key causes align with AI workflow dynamics and hardware compatibility, including:
- Underpowered CPUs: Weak single-core performance or insufficient cores failing to keep up with data-hungry NVIDIA GPUs (e.g., H200’s 141GB HBM3e memory demanding fast data transfer);
- Limited PCIe bandwidth: Older PCIe 3.0/4.0 slots restricting data flow between CPU and modern NVIDIA GPUs (e.g., RTX 4090/ H200 optimized for PCIe 5.0);
- Inefficient data preprocessing: CPU-bound tasks (e.g., dataset loading, tokenization for LLMs) delaying data delivery to the GPU;
- Poor resource allocation: Overloading a single CPU with multiple high-performance GPUs (e.g., pairing one CPU with 4x A100s) without load balancing.
3. How to calculate if an AI workload is experiencing a CPU-GPU bottleneck, and how does WhaleFlux assist?
Identify bottlenecks using three key metrics, with WhaleFlux streamlining measurement:
- GPU Utilization: Consistently low GPU usage (<50%) while the CPU is maxed out (≥80%) indicates a CPU bottleneck;
- Data Transfer Latency: Slow data movement between CPU and GPU (measured via NVIDIA NVLink/PCIe bandwidth tools);
- Task Queue Backlog: Stalled AI tasks (e.g., LLM inference batches) waiting for CPU processing.
WhaleFlux simplifies calculation with built-in monitoring: It tracks real-time CPU/GPU metrics (utilization, latency, data throughput) across NVIDIA GPU clusters, generates bottleneck alerts, and provides visual dashboards to pinpoint whether the CPU or data transfer is the limiting factor.
4. How does WhaleFlux fix and optimize CPU-GPU bottlenecks for NVIDIA GPUs?
WhaleFlux resolves bottlenecks through AI-focused cluster optimization, tailored to NVIDIA GPU capabilities:
- Intelligent Resource Scheduling: Distributes CPU-bound tasks (e.g., data preprocessing) across idle CPU cores, ensuring NVIDIA GPUs (e.g., A100/RTX 4090) receive a steady data stream without waiting;
- PCIe Bandwidth Optimization: Prioritizes data routing for PCIe 5.0-enabled NVIDIA GPUs (e.g., H200/RTX 4090) and balances workloads to avoid lane congestion;
- Workload Offloading: Shifts non-critical CPU tasks to underutilized nodes, freeing up core CPU resources to feed high-performance NVIDIA GPUs;
- GPU-CPU Matching: Recommends CPU upgrades or GPU adjustments (e.g., pairing H200 with high-core-count CPUs) via WhaleFlux’s workload analysis, ensuring hardware alignment.
These steps typically reduce bottleneck impact by 60%+, boosting NVIDIA GPU utilization and LLM deployment speed.
5. For long-term AI efficiency, how can enterprises avoid CPU-GPU bottlenecks with WhaleFlux and NVIDIA GPUs?
Combine WhaleFlux’s capabilities with proactive hardware and workflow planning:
- Right-Size Hardware Pairing: Use WhaleFlux’s workload analysis to match CPUs with NVIDIA GPUs (e.g., H200/A100 with high-performance, multi-core CPUs; RTX 4060 with mid-range CPUs for lightweight inference);
- Optimize Cluster Configuration: Leverage WhaleFlux to design clusters with sufficient PCIe 5.0 slots (for modern NVIDIA GPUs) and distribute GPUs across nodes to avoid overloading single CPUs;
- Streamline Data Workflows: Integrate WhaleFlux with NVIDIA AI frameworks (e.g., PyTorch/TensorFlow) to offload preprocessing to GPUs where possible (e.g., using Tensor Cores for tokenization);
- Flexible GPU Procurement: Purchase or lease NVIDIA GPUs via WhaleFlux (hourly rental not available) to scale hardware in line with CPU capabilities – e.g., adding RTX 4090s instead of overloading existing CPUs with H200s.
WhaleFlux’s ongoing cluster optimization ensures CPU-GPU synergy is maintained as AI workloads (e.g., larger LLMs) evolve, reducing cloud computing costs while preserving performance.