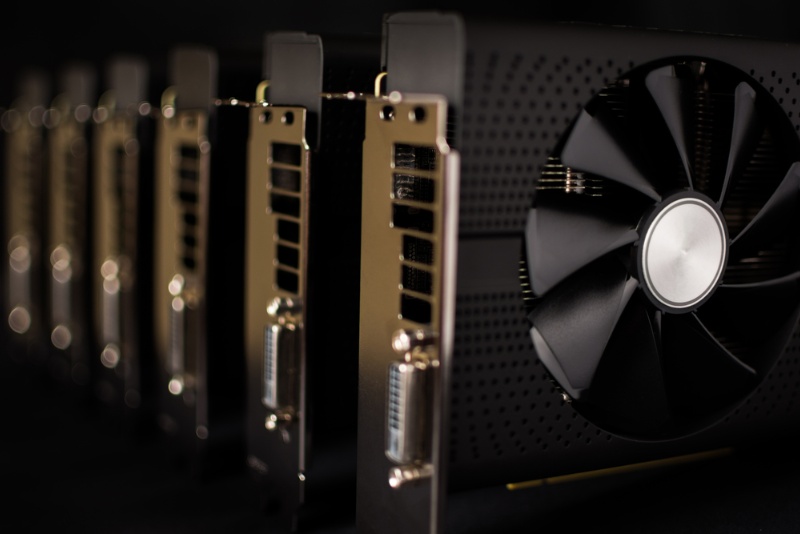
1. The Great Terminology Mix-Up: “Is a GPU the Graphics Card?”
When buying tech, 72% of people use “GPU” and “graphics card” interchangeably. But in enterprise AI, this confusion costs millions. Here’s the critical distinction:
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): The actual processor chip performing calculations (e.g., NVIDIA’s AD102 in RTX 4090).
- Graphics Card: The complete hardware containing GPU, PCB, cooling, and ports.
WhaleFlux Context: AI enterprises care about GPU compute power – not packaging. Our platform optimizes NVIDIA silicon whether in flashy graphics cards or server modules.
2. Anatomy of a Graphics Card: Where the GPU Lives
- GPU: AD102 chip
- Extras: RGB lighting, triple fans, HDMI ports
- Purpose: Gaming/rendering
Data Center Module (e.g., H100 SXM5):
- GPU: GH100 chip
- Minimalist design: No fans/displays
- Purpose: Pure AI computation
Key Takeaway: All graphics cards contain a GPU, but data center GPUs aren’t graphics cards.
3. Why the Distinction Matters for Enterprise AI
Consumer Graphics Cards (RTX 4090):
✅ Pros: Affordable prototyping ($1,600)
❌ Cons:
- Thermal limits (88°C throttling)
- No ECC memory → data corruption risk
- Unstable drivers in clusters
*Data Center GPUs (H100/A100):*
✅ Pros:
- 24/7 reliability with ECC
- NVLink for multi-GPU speed
- Optimized for AI workloads
⚠️ Hidden Cost: Using RTX 4090 graphics cards in production clusters increases failure rates by 3x.
4. The WhaleFlux Advantage: Abstracting Hardware Complexity
WhaleFlux cuts through the packaging confusion by managing pure GPU power:
Unified Orchestration:
- Treats H100 SXM5 (server module) and RTX 4090 (graphics card) as equal “AI accelerators”
- Focuses on CUDA cores/VRAM – ignores RGB lights and fan types
Optimization Outcome
Achieves 95% utilization for all NVIDIA silicon
- H100/H200 (data center GPUs)
- A100 (versatile workhorse)
- RTX 4090 (consumer graphics cards)
5. Optimizing Mixed Environments: Graphics Cards & Data Center GPUs
Mixing RTX 4090 graphics cards with H100 modules creates chaos:
- Driver conflicts crash training jobs
- Inefficient resource allocation
WhaleFlux Solutions:
Hardware-Agnostic Scheduling:
- Auto-assigns LLM training to H100s
- Uses RTX 4090 graphics cards for visualization
Stability Isolation:
- Containers prevent consumer drivers from crashing H100 workloads
Unified Monitoring:
- Tracks GPU utilization across all form factors
Value Unlocked: 40%+ cost reduction via optimal resource use
6. Choosing the Right Compute: WhaleFlux Flexibility
Get GPU power your way:
| Option | Best For | WhaleFlux Management |
| Rent H100/H200/A100 | Enterprise production | Optimized 24/7 with ECC |
| Use Existing RTX 4090 | Prototyping | Safe sandboxing in clusters |
Key Details:
- Rentals require 1-month minimum commitment
- Seamlessly integrate owned graphics cards
7. Beyond Semantics: Strategic AI Acceleration
The Final Word:
- GPU = Engine
- Graphics Card = Car
- WhaleFlux = Your AI Fleet Manager
Key Insight: Whether you need a “sports car” (RTX 4090 graphics card) or “semi-truck” (H100 module), WhaleFlux maximizes your NVIDIA GPU investment.
Ready to optimize?
1️⃣ Audit your infrastructure: Identify underutilized GPUs
2️⃣ Rent H100/H200/A100 modules (1-month min) via WhaleFlux
3️⃣ Integrate existing RTX 4090 graphics cards into managed clusters
Stop worrying about hardware packaging. Start maximizing AI performance.
FAQs
1. Is a GPU the same as a graphics card, especially for NVIDIA hardware? Does WhaleFlux distinguish between them?
No—they are related but distinct. A GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is the core computing component responsible for parallel processing (e.g., AI tasks, rendering). A graphics card (or video card) is the complete hardware device that houses the GPU, plus supporting components like memory (HBM3/GDDR6X), cooling systems, and PCIe connectors. For NVIDIA, examples include: the NVIDIA H200 GPU is the core of an H200-based graphics card, and the RTX 4090 GPU is integrated into the RTX 4090 graphics card.
WhaleFlux focuses on optimizing the NVIDIA GPUs within graphics cards, as they are the engine for AI workloads. The tool provides access to full NVIDIA graphics cards (equipped with high-performance GPUs like H200, A100, RTX 4090) for purchase or long-term lease (hourly rental not available), and its cluster management capabilities maximize the efficiency of the GPUs inside these graphics cards.
2. What role do GPUs vs. graphics cards play in AI workloads, and how does WhaleFlux enhance their synergy?
Their roles are complementary, with WhaleFlux bridging hardware and performance:
- GPU: The “brain” that executes AI tasks (LLM training/inference) via NVIDIA’s CUDA/Tensor Cores. Key for AI are specs like tensor computing power and memory capacity (e.g., H200 GPU’s 141GB HBM3e).
- Graphics Card: The “body” that delivers the GPU’s capabilities—providing power, cooling, and connectivity to ensure the GPU runs reliably (critical for 7×24 enterprise AI).
WhaleFlux enhances synergy by: ① Monitoring both GPU performance (utilization, latency) and graphics card health (temperature, power draw) to prevent overheating or bottlenecks; ② Optimizing task distribution across NVIDIA graphics cards to leverage their GPUs’ strengths (e.g., assigning large-scale training to H200-equipped cards, inference to RTX 4090 cards); ③ Ensuring graphics cards are configured for AI (e.g., enabling ECC memory on A100-based cards) to maximize GPU stability.
3. Can any NVIDIA graphics card be used for AI, or does it depend on the GPU inside? How does WhaleFlux help select the right one?
AI suitability depends on the GPU inside the NVIDIA graphics card—not all graphics cards are equal for AI. For example:
- Graphics cards with AI-optimized GPUs (H200, A100, RTX A6000) excel at training/inference, thanks to ECC memory and high tensor computing power.
- Graphics cards with gaming-focused GPUs (RTX 4090, 4060) work for lightweight AI (prototyping, small-model inference) but lack enterprise-grade features for large-scale tasks.
WhaleFlux simplifies selection by: ① Mapping AI workloads (e.g., 100B+ parameter LLMs) to graphics cards with compatible NVIDIA GPUs (e.g., H200/A100-based cards); ② Offering a full lineup of NVIDIA graphics cards (from RTX 4060 to H200) for purchase/lease; ③ Providing workload analysis to recommend cards that balance GPU performance (e.g., tensor cores) and practicality (e.g., power consumption).
4. How does WhaleFlux manage NVIDIA GPUs and graphics cards in AI clusters, given their distinct roles?
WhaleFlux’s cluster management tools treat NVIDIA graphics cards as the hardware vessel and GPUs as the computational core—optimizing both layers for AI efficiency:
- GPU-Level Optimization: Allocates AI tasks to specific NVIDIA GPUs (e.g., H100 vs. RTX 4090) based on their computing power and memory, ensuring no GPU is underutilized.
- Graphics Card-Level Management: Monitors supporting components (cooling, power supply) to prevent issues that would throttle the GPU (e.g., overheating on RTX 4090 cards).
- Seamless Scaling: When adding capacity, WhaleFlux integrates new NVIDIA graphics cards (and their GPUs) into existing clusters without reconfiguration, maintaining workflow continuity.
- Cost Control: By optimizing GPU utilization across graphics cards, WhaleFlux reduces cloud computing costs by up to 30% compared to unmanaged clusters.
5. For enterprises new to AI, how does WhaleFlux clarify GPU/graphics card terminology while ensuring they get the right NVIDIA hardware?
WhaleFlux removes confusion and streamlines hardware selection through three key support features:
- Simplified Terminology Guidance: Clearly links “AI-ready NVIDIA graphics cards” to their core GPUs (e.g., “H200 graphics card = H200 GPU + enterprise cooling/power”) in its documentation and dashboards.
- Customized Recommendations: Asks enterprises to define AI goals (e.g., “small-scale inference” vs. “LLM training”) and recommends specific NVIDIA graphics cards (e.g., RTX 4090 for startups, A100 for enterprises) based on their GPU capabilities.
- End-to-End Support: From purchasing/leasing NVIDIA graphics cards to configuring their GPUs in clusters, WhaleFlux provides a unified platform—eliminating the need to separate GPU and graphics card management.
This approach ensures enterprises focus on AI performance, not terminology, while leveraging WhaleFlux’s expertise to select the right NVIDIA hardware.